The recent Belgium LifeWatch Biodiversity Day 2024 held on 30 January shed light on the important theme of taxonomy, underscoring the significance of scientifically naming newly discovered species. Understanding a species' name unlocks a trove of knowledge about its biology, distribution, and significance to humanity. Generally speaking, this information serves as a cornerstone across various domains, including supporting medical research, advancing bioinformatics and genomic research, enhancing agricultural practices, and identifying crucial biodiversity "hotspots" for prioritised protection.
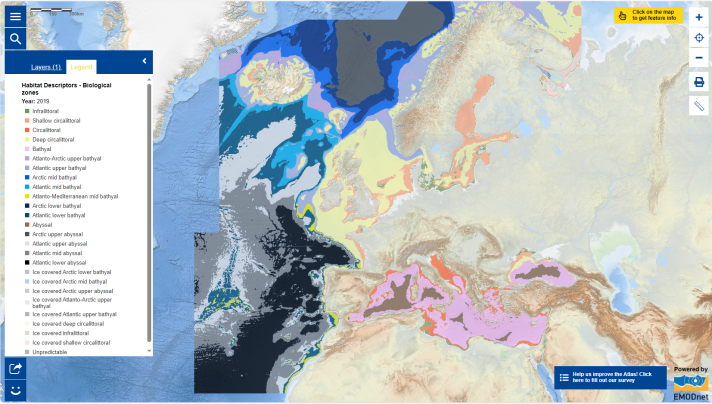
While we celebrate the richness of biodiversity, it is crucial to acknowledge its degradation, largely attributed to human activities. Collective efforts on environmental and ocean protection and preservation are imperative, but equally important is understanding the habitats where organisms thrive, providing the foundation of biodiversity conservation. For this purpose, this week, we explore the biological zones of the sea. Biological zones are determined using a variety of physical variables and proxies (data used to study a situation, phenomenon or condition for which no direct information is available [1]). The Map of the Week shows the classified biological zones for all European waters used in the EMODnet broad-scale seabed habitat model (EUSeaMap). It is one of the several habitat descriptors used to determine the final habitat type. By gaining insights into the diverse ecosystems present, we pave the way for informed conservation strategies. These efforts are essential in maintaining the delicate balance that sustains the vast array of life forms thriving beneath the ocean's surface.
To take meaningful actions in safeguarding ocean biodiversity, it is necessary to understand the importance of marine ecosystems and the scientific reasons behind the decline in biodiversity. Actions can then include getting involved in conservation projects and promoting ocean knowledge. Every little effort, when joined by others, creates a ripple effect that fosters a healthier, more biodiverse ocean for future generations.
Wish to learn more about biodiversity and biodiversity policies?
- Explore the Map of the Week by clicking on the different zones on the map;
- Have a look at the training and educational resources provided by LifeWatch ERIC (European Research Infrastructure Consortia);
- Dive into the UNESCO Ocean Literacy Portal’s Teacher Area;
- Read about the European Union Biodiversity strategy for 2030;
- Learn more about the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) adopted during COP15 to the United Nations Convention of Biological Diversity (CBD);
- Find out about the agreement under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea on the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity of areas beyond national jurisdiction (BBNJ Agreement), also known as the “Treaty of the High Seas”
The data in this map are provided by EMODnet.
[1] https://www.eea.europa.eu/help/glossary/eea-glossary/proxy-indicator