Survey of practitioners
Survey (still you can reply)
Summary of first 47 replies
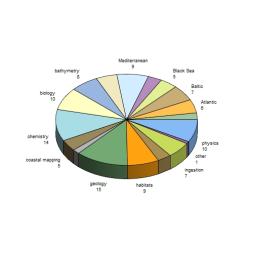
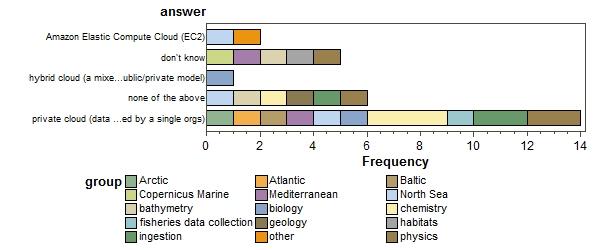
Where are you coming from? (more than one answer per respondent allowed) (click to enlarge)
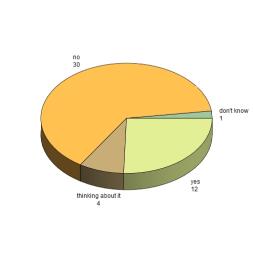
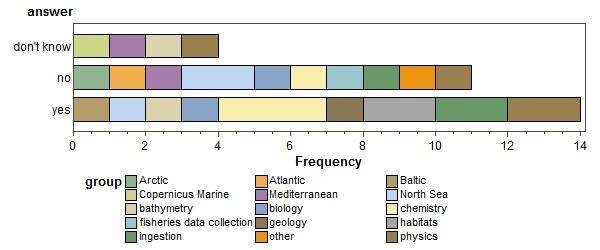
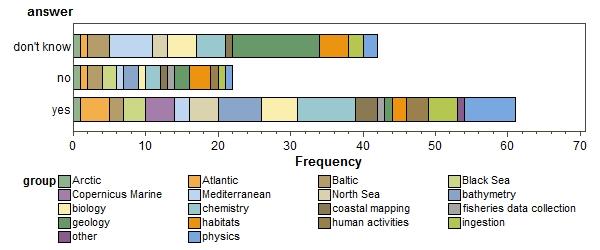
Do you use the Cloud now? (click to enlarge)
 |
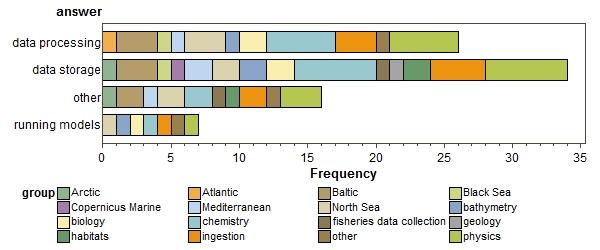
what for? more than one answer allowed)
can you give details?
| Obs | groups | value_c |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | North Sea;geology | documents not related to official projects within Geological Survey of the Netherlands are store in and accessible through cloud |
| 2 | habitats | Currently we only upload data to the cloud when we want to share it with others. However, in the next couple of years my organisation (JNCC) plans to move all of our data onto the cloud - they are currently deciding between AWS and Windows Azure. |
| 3 | habitats | Our organisation uses Office software hosted in a cloud and there are plans to store our main spatial data holding in a cloud |
| 4 | biology | Part of data infrastrucutre interacts with Lifewatch cloud/EGI |
| 5 | Atlantic;North Sea;biology | R shiny applications on a web server |
| 6 | Copernicus Marine;Mediterranean;bathymetry;physics | It depends what you mean by Cloud. I think everybody is using the cloud without necessarily knowing it. So if it's not properly defined right from the beginning, the goal is not clear. |
| 7 | bathymetry;chemistry;ingestion;physics | In several of the EMODnet projects and in SeaDataCloud we are moving into the big data domain. Right now still a lot of computations such as processing with DIVA and ODV for EMODnet Chemistry and SeaDataCloud and with GLOBE for EMODnet Bathymetry are done by regional coordinators with office computers. However the volumes of data are growing and therefore people have to divide their areas in tiles in order to meet the capacity of their computers. This makes the processing more cumbersome, including edge issues, and takes a lot of time. Moreover we want to tune the work and computations between the regions in order to get seamless products. This requires options for collaboiation. Moreover we would like to compare the previous products with new products and see the differences, e.g by means of 3 D viusualisations. However the present machines do not provide sufficient power for these kind of actions which will improve considerably the overall quality of the products. For that reason we are exploring and making our first steps into cloud computing and virtual research environments whereby we will bring both the data and the applications (DIVA, ODV, GLOBE, Visualisations ..) to the cloud and make use of High Performance Computing. This way we strive for shorter cycles for producing data products but also for higher quality as there should be more functionality and capabilities and pure computing power to handle more data and all kinds of comparisons and visualisations. In the mentioned projects we are working together with Academic Computing Centres in Europe, united in the EUDAT consortium, and also with Datarmor, a regional cloud and HPC infrastructure of IFREMER and Shom. Moreover we are tuning our developments with comparable projects in USA (NOAA, private sector, ..) and Australia (Nectar) as part of the ODIP II project where we have a prototype ;Digital playground'. In the cloud we are developing Virtual Research Environments which could support specific workflows and their communities. Thereby we have User Interfaces for the researchers and API's between the different applications as part of the Workflows. Moreover there are i-notebook applications (Yupiter) for more expert users. As coordinator / technical coordinator of many data management projects and infrastructures I am fully convinced that we have to make the next step in our thinking and acting by embracing and exploring the virtues of the cloud.Waiting means standing still and being overtaken by others. As we know from ODIP we are already behind in this field in Europe and have to catch up. This will open new opportunities for our work. For that we should work as marine discipline data infrastructures (such as SeaDataNet, EurOBIS, ..) with e-infrastructures (big storage and computing facilities) as a good combination. The discipline should lead the developments from their content knowledge while the e-infrastructures should support with technical facilities. Within this terrain we are also exploring new tools like Elastic Search, neural networks, 3D visualisations, SWE ingestion, and others that might provide extra functionality and performance. We are starting with controlled environments aiming at our interanl workflows and products. However in a later stage it is planned to make the virtual spaces with the access to big data and dedicated applications more widely accessible for users, thereby bringing users to the cloud and striving for 'no more downloading' but using data on the spot for generating products. |
| 8 | Baltic;ingestion;physics | data download buffering |
| 9 | chemistry | EMODnet Chemistry uses the Cloud provided by Cineca to store the regional aggregated data sets and to process the OGC viewing services avilable on Chemistry portal. |
| 10 | Arctic;Mediterranean;chemistry;fisheries data collection;ingestion;physics | All my data and documentataion have been stored in remote Cloud (VPS) firstly because of security reason. |
| 11 | Black Sea;Mediterranean;chemistry;physics | computing 3D-4D fields (climatologies) from unevenly distributed observation data |
| 12 | Baltic;North Sea;chemistry;physics | Will do within the project Seadatacloud |
what technology?
do you have a dedicated team to manage it?
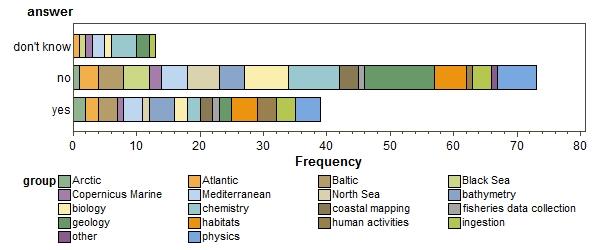
are any of your datasets getting too big to handle
which ones?
| Obs | groups | value_c |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arctic;Atlantic;North Sea;biology;coastal mapping;habitats | GIS raster datasett for distribution modelling are getting big, as we are working more and more on European and global level. |
| 2 | Baltic;bathymetry;geology;habitats | Water column data from multibeam and bathymetry gridding |
| 3 | Mediterranean;habitats | video transects on benthic habitats recorded by ROV in 4k |
| 4 | Atlantic;bathymetry;coastal mapping;geology | bathymetry, aerial photography (data collected by boats, planes & drones) |
| 5 | human activities | We'll have to develop a vessel density map of EU waters. A couple of terabytes of data. |
| 6 | Baltic;biology;habitats;human activities | large biodiversity datasets e.g. from mapping projects |
| 7 | Copernicus Marine;Mediterranean;bathymetry;physics | numerical model outputs, can grow very fast and result in Teras for one day of data. |
| 8 | bathymetry;chemistry;ingestion;physics | Chemistry data collections; bathymetry data sets; E.g. in Bathymetry we are increasing the coverage area and the resolution of the target DTM to 1/8 arc minute = ca 125 meters grid. The present DTM already has the following number of grid nodes: 1.092.115.678 (28.799 rows x 37.922 columns). In the new project this will be circa 10 times more grid cells while regional coordinators and integrator already had problems handling the volume in the previous round. |
| 9 | Baltic;ingestion;physics | opeational gridded data (e.g. HFR, real time underwater noise stream, operational T&S maps, etc) |
| 10 | Arctic;Mediterranean;chemistry;fisheries data collection;ingestion;physics | meteo-ocean real time data (buoys and coastal meteo-ocean stations, sealevel, HF radars), underwater noise data, sea-currents data, model outputs data |
| 11 | human activities | We'll have to develop a vessel density map of EU waters. A couple of terabytes of data. |
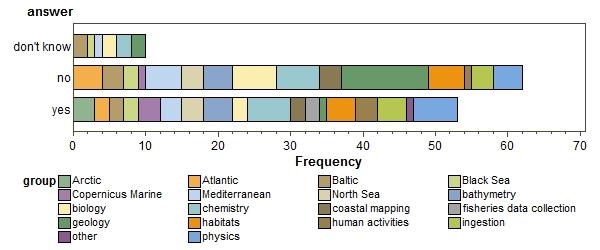
are any of your processes limited by computing power?
which ones?
| Obs | groups | value_c |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | habitats | Spatial analysis |
| 2 | Arctic;Atlantic;North Sea;biology;coastal mapping;habitats | Large scale spatial analyses require good computer memory and capacity. |
| 3 | Arctic;Atlantic;Copernicus Marine;North Sea;bathymetry;biology;chemistry;coastal mapping;fisheries data collection;habitats;human activities;physics | GIS-dataset or data that needs to be processed to assimilate into GIS. |
| 4 | Baltic;bathymetry;geology;habitats | Processing side-scan data and bathymetry |
| 5 | human activities | To make this map, either we buy a new machine or we use a cloud. Second option is preferred for obvious reasons. |
| 6 | chemistry | Generating gridded data products |
| 7 | Copernicus Marine;Mediterranean;bathymetry;physics | - numerical modelling due to fine resolution of the grid model. - spatial interpolation requires very fine grids In both cases we must either use a less fine resolution of work on sub-domains. |
| 8 | bathymetry;chemistry;ingestion;physics | See explanation above about DIVA, ODV and GLOBE. The limitations are solved by dividing the areas in tiles and later stitching these together . But this gives edge effects etc. |
| 9 | Baltic;ingestion;physics | plotting multiple big data time series |
| 10 | Black Sea;Copernicus Marine;chemistry;ingestion | near real time quality control procedure |
| 11 | Arctic;Mediterranean;chemistry;fisheries data collection;ingestion;physics | There is no related data. Only related numerical modelling. |
| 12 | Black Sea;Mediterranean;chemistry;physics | computing 4D climatologies, running averages etc. |
| 13 | human activities | vessel density map |
do you think any data processing software could be put on the cloud for general use?
what would this software do? (try to be precise yet comprehensible by the general public). If there is more than one software, could you make a separate submission?
| Obs | groups | value_c |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | North Sea;other | Numerical modelling with user-friendly interfaces. Post processing of observation datasets to produce derived products. |
| 2 | Copernicus Marine | create temporal average grid data from Copernicus archives |
| 3 | Atlantic;bathymetry;biology;coastal mapping;habitats | 1 - upscaling (resolution refinement) of environmental layers 2 - interpolation (e.g. trilinear) of environmental data from oceanographic grids to associate with biological occurrences |
| 4 | Arctic;Atlantic;Copernicus Marine;North Sea;bathymetry;biology;chemistry;coastal mapping;fisheries data collection;habitats;human activities;physics | Yes, this could potentially be done. But if it comes at the cost of transporting data to and fro the cloud, changing formats, learning and ajdusting to new software and workflows, it will very likely be detrimental to my productivity. |
| 5 | Atlantic;bathymetry;coastal mapping;geology | Gridding software to produce DTM's and Geotiffs with options to export to all standard formats. |
| 6 | human activities | A relational database management system (e.g. SQLite). ArcGIS |
| 7 | biology | model species distributions |
| 8 | chemistry | Creating gridded data products from in situ observations DIVA (Data-Interpolating Variational Analysis) |
| 9 | bathymetry;biology;chemistry;ingestion;physics | Don't know. The question was "any data processing software could be put on the cloud " and my answer is 'yes' |
| 10 | Atlantic;North Sea;biology | web services producing basic output from data bases, e.g. maps of distribution of species as derived from biological data bases |
| 11 | Black Sea | Our intentions are in conjunction with SeaDataCloud project (2016-2020), grant agreement 730960, EU H2020 programme, which aims at considerably advancing SeaDataNet Services and increasing their usage, adopting cloud and High Performance Computing technology for better performance. |
| 12 | Copernicus Marine;Mediterranean;bathymetry;physics | Model for weather and ocean circulation forecast. |
| 13 | bathymetry;chemistry;ingestion;physics | see story above |
| 14 | Baltic;ingestion;physics | data processing and interpolation for producing operational gridded products on physical parameters |
| 15 | chemistry | Any software used for data management, from authentication, insert and query, quality control, processing and visualisation. |
| 16 | Black Sea;Copernicus Marine;chemistry;ingestion | quality control procedures, data mining |
| 17 | Black Sea;Mediterranean;chemistry;physics | Selection and aggregation of data. Visualization, quality control and analysis of data. Computation of products from data, such as 3D-4D fields, climatologies, timeseries etc. |
| 18 | human activities | SQLite, ArcGIS, QGIS |
| 19 | Baltic;North Sea;chemistry;physics | Definately. For example software the might cause problems installing on different OS. Software in the cloud would always be the latest version and no need to constantly update on your machine. Far superior computation power possible compared to your laptop. Easy sharing of datasets processed in the cloud if storing is possible. What would it do? Everything you could do with data. Processing, visualisation, analysing, quality control, etc. |
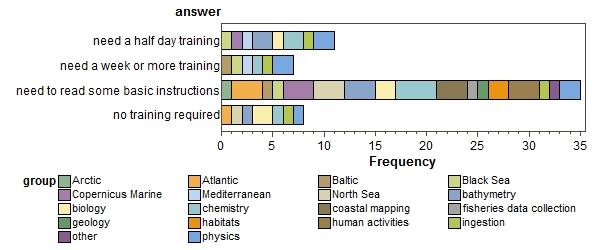
how easy to use for target users (scientifically literate)
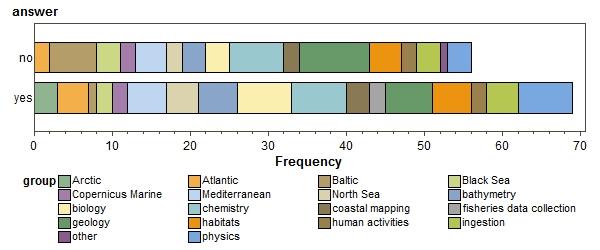
Would putting databases on the cloud allow sharing of maintenance burden with other organisations?
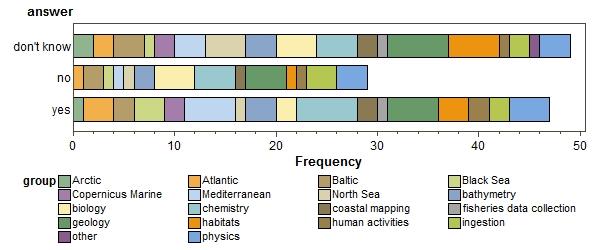
Do you have concerns about aspects of privacy, confidentiality or security of data on cloud?
what are your concerns?
| Obs | groups | value_c |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | North Sea;geology | no control over / influence on security |
| 2 | Arctic;Atlantic;North Sea;biology;coastal mapping;habitats | Not being very familiar with cloud data I am concerned about the security of data as this feels like a place that we do not have control over. |
| 3 | habitats | Data under license or concerning sensitive species would not be given correct role permissions. |
| 4 | Atlantic;bathymetry;biology;coastal mapping;habitats | Hackers and rogue data managers |
| 5 | geology | ise of data, data being digested in databases that then will be digested by others databases and then get lost |
| 6 | Arctic;Atlantic;Copernicus Marine;North Sea;bathymetry;biology;chemistry;coastal mapping;fisheries data collection;habitats;human activities;physics | My own personal and or professional privacy, confidentiality of data processed in the cloud, security issues including data integrity of data stored in the cloud. |
| 7 | geology | Restricted status of original dataset and security |
| 8 | Mediterranean;geology | Some data are confidential and it would not be possible to be in public view. Moreover, our Department has concerns regarding potential cyber-attacks on our data if they are available on cloud. Furthermore, there are some legal obstacles related to the governmental status of our Department. |
| 9 | biology | private data |
| 10 | Baltic;biology;habitats;human activities | quality control of data, maintenance of data if located in several places |
| 11 | Black Sea | N/A |
| 12 | bathymetry;biology;chemistry;ingestion;physics | Given American privacy laws (or the lack of it) and the fact that American law considers data on servers built with American hardware and/or software to be practically 'owned' by the US, this is a big concern. |
| 13 | Atlantic;North Sea;biology | data integrity. Access more difficult to control than on private servers |
| 14 | geology | All of the above and the presumed difficulty in switching service providers without compromising data. |
| 15 | Copernicus Marine;Mediterranean;bathymetry;physics | For scientific data it's probably okay, but for health data, there is a risk for privacy breach that could have a direct, negative impact on people. Anonymisation is really needed. |
| 16 | bathymetry;chemistry;ingestion;physics | we need to have good account management with different roles for users that have different priviledges. |
| 17 | chemistry | Data confidentiality, data policy |
| 18 | Mediterranean;chemistry;geology;ingestion;physics | the data is like a currency for research institutions. If abused or used without given credit to its creators is like taking credentials to the research work. |
| 19 | Arctic;Mediterranean;chemistry;fisheries data collection;ingestion;physics | all is out our control (only selected data and information to be uploud on cloud on remote system) |
| 20 | Black Sea;Mediterranean;chemistry;physics | There are categories of data that can be shared under certain contitions, e.g. data under moratorium or data that can be shared to a user only in case of joint activities etc. For the moment the decision is taken by data holder individually in each case. It is not clear how this can be controlled if such data will be in Cloud. |
what time-consuming processes could not be put on the Cloud?
| Obs | groups | value_c |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | North Sea;geology | don't know |
| 2 | Arctic;Atlantic;North Sea;biology;coastal mapping;habitats | Analyses of high resolution bathymetric data that are classified by the Ministry of defence for state security reasons. |
| 3 | North Sea;other | General activities less appropriate for the cloud tend to be those with high user flexibility and those which are necessary with data locally. However, it can be very easy getting a virtual machine on the cloud and using it as though it were part of a local software estate. |
| 4 | habitats | Processes requiring large amounts of data in/egress. Manual digitising of spatial data. |
| 5 | habitats | any manual metadata input |
| 6 | Black Sea;bathymetry;coastal mapping;geology | I don't know. We don't have this problem. |
| 7 | Atlantic;bathymetry;biology;coastal mapping;habitats | semi-automated annotation of biological or geological occurrences in archive underwater video and photo datasets |
| 8 | Baltic;bathymetry;geology;habitats | All backscatter data processing software are restricted to license limitations. Also bathymetry data handeling and cleaning as well as gridding. |
| 9 | geology | Digitising old Russian data |
| 10 | geology | Digitising maps, Data base management... |
| 11 | human activities | Don't know. |
| 12 | biology | data standardizations + quality control |
| 13 | chemistry | "The cloud" are just computers administered by somebody else. There is no real fundamental limitation was could be done on "the cloud". |
| 14 | Black Sea | N/A |
| 15 | Atlantic;North Sea;biology | All collection of biological data that is based on written material (publications, hand-written logs, etc.) This includes some of the most important material, such as traits of species. |
| 16 | Copernicus Marine;Mediterranean;bathymetry;physics | no idea |
| 17 | Mediterranean;chemistry | Don't know |
| 18 | Atlantic;chemistry | data in deprecated formats or in non numeric formats (e.g., pdf files) |
| 19 | chemistry | Any manual insert of meta-data and data |
| 20 | Mediterranean;chemistry;geology;ingestion;physics | Not sure yet. First I have to understand the Cloud system. |
| 21 | Black Sea;Copernicus Marine;chemistry;ingestion | oceanographics models |
| 22 | Arctic;Mediterranean;chemistry;fisheries data collection;ingestion;physics | there is no such data |
| 23 | Black Sea;Mediterranean;chemistry;physics | Raw data processing (e.g. from ADCP) when total Cloud-procedures time does not give significant advance on traditional processing time, particularly taking into account that after being processed raw data practically are not re-used. |
| 24 | human activities | harmonization is often a process that require to worl locally |
| 25 | Baltic;North Sea;chemistry;physics | Why not digitising old Russian data logs? Could be done in the cloud for directly insertion into a shared database. Anything you can do on a laptop or a server could also be done in the Cloud, except work that you do on a laptop or server which is offline. For example work far out at sea where you might lack an internet connection, or at least one fast enough to work against the cloud. |
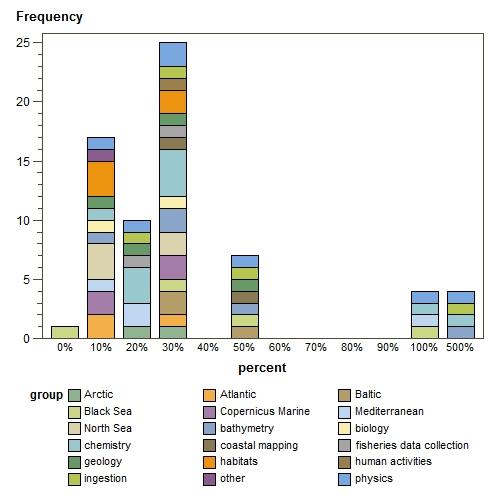
what would be increase in your performance through more use of Cloud ? (percent)
Sorry, there was a problem with the Graph control or plug-in in your browser.The graph "Bar chart of percent" cannot be displayed.